Did you know that beer withdrawal is a serious condition that millions of people face every year? Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial to ensure a safe and successful recovery. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve deep into the world of beer withdrawal, debunk common myths, and explore the importance of ongoing support in maintaining sobriety.
Key Takeaways
- Beer withdrawal is a serious condition caused by an imbalance of GABA in the brain, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe.
- Treatment options for managing beer withdrawal include medical supervision and detox, outpatient/inpatient programs, support groups and counseling.
- Prevention strategies such as responsible drinking habits are essential for avoiding potential complications of beer withdrawal during long term recovery process.
Beer Withdrawal: What You Need to Know

Beer withdrawal is a type of alcohol withdrawal that occurs when a person with a chronic alcohol use disorder suddenly stops or significantly reduces their beer intake. It is estimated that around two million Americans experience alcohol withdrawal syndrome every year, and symptoms can range from mild to severe. Given its widespread impact, understanding the symptoms and available treatment options is key to a safe and successful recovery.
The severity of beer withdrawal is influenced by various factors, including:
- Molecular and genetic mechanisms
- The clinical significance of kindling
- Risk factors for more severe withdrawal
- Methods to encourage patients to continue with relapse prevention
Treatment options for alcohol withdrawal are determined based on the patient’s score on the CIWA-Ar test and can take place in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
The Connection Between Beer and Alcohol Withdrawal
Though beer withdrawal is a specific type of alcohol withdrawal, it shares many similarities with general alcohol withdrawal. Both conditions result from the disruption of brain chemistry due to alcohol use, causing heightened neural activity when alcohol is withheld. Symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild to severe and can include tremors, sweating, and nausea. It is crucial to recognize alcohol withdrawal symptoms and have alcohol withdrawal diagnosed by a medical professional to ensure proper treatment and care, especially when experiencing alcohol withdrawal.
The physical and mental effects of alcohol and beer withdrawal on the central nervous system are primarily caused by an imbalance of GABA in the brain, resulting in an adjustment of neurotransmitter production to accommodate the influence of alcohol. When alcohol use is discontinued, the brain’s chemical balance is disturbed, leading to withdrawal symptoms. That’s why seeking medical help during acute alcohol withdrawal is crucial, as quitting without assistance may result in life-threatening complications.
Symptoms of Beer Withdrawal

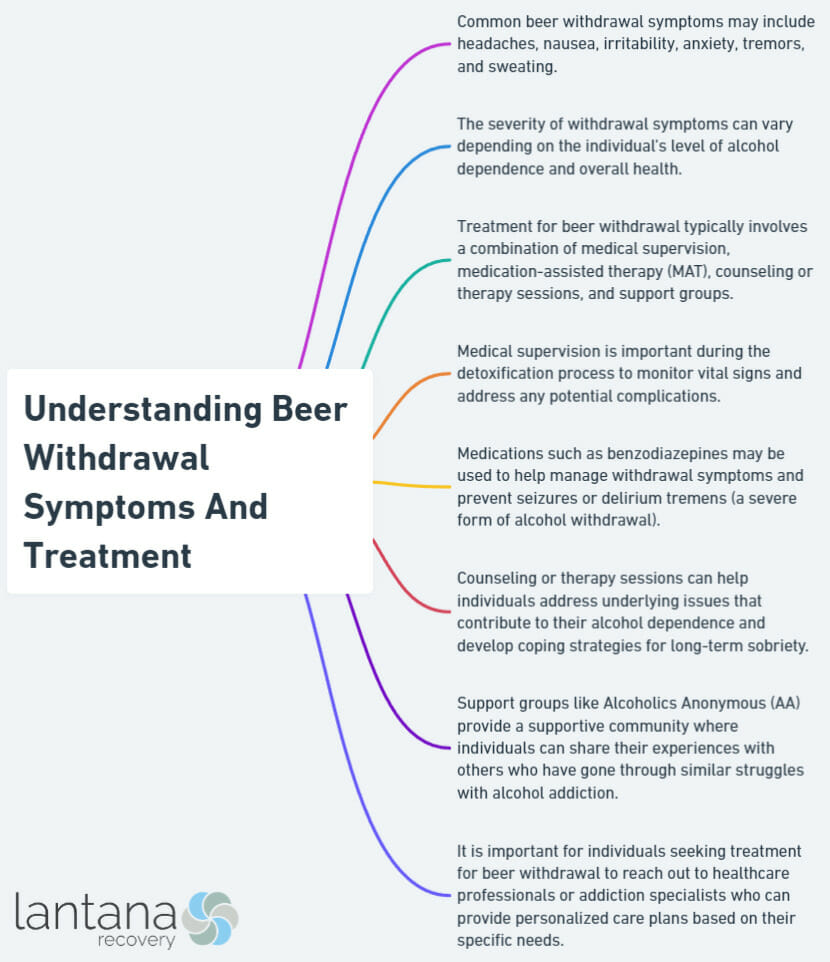
The symptoms of beer withdrawal can be both physical and emotional, with some individuals experiencing anxiety, bad dreams, depression, and difficulty thinking clearly. Physical symptoms may include tremors, sweating, nausea, and high blood pressure. Recognizing these symptoms early is vital for implementing the appropriate treatment measures.
Alcohol withdrawal can be categorized into three stages, ranging from mild to severe symptoms. The following subsections will delve into the various symptoms experienced during beer withdrawal.
Mild Beer Withdrawal Symptoms
Mild beer withdrawal symptoms are generally less severe than those experienced during moderate to severe withdrawal. Common mild symptoms may include headache, anxiety, and irritability, which can also be considered as common withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms often resemble a hangover but persist for longer than a single day.
Mild withdrawal symptoms typically begin within 6 to 12 hours after a person stops drinking. Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking necessary treatment is paramount.
Moderate to Severe Beer Withdrawal Symptoms
More severe beer withdrawal symptoms can include seizures, hallucinations, and delirium symptoms, which can be life-threatening. Heavy alcohol users are at a greater risk for hallucinations or nightmares during alcohol withdrawal, with a 2.4-fold higher likelihood than moderate or light alcohol users.
Symptoms of delirium tremens (DTs) can manifest within 48–96 hours after stopping alcohol consumption and can be characterized by severe withdrawal symptoms that may be fatal. Withdrawal seizures, sometimes referred to as “rum fits,” can occur between 6–48 hours after the last use and are characterized by seizures in individuals with no prior history of seizures.
For a safe recovery, it’s necessary to recognize these symptoms and seek immediate medical attention.
Factors Influencing Beer Withdrawal Severity

Various factors contribute to the severity of beer withdrawal, including drinking habits, duration of alcohol use, and individual health conditions. A greater risk of more severe withdrawal symptoms is associated with more severe alcohol dependence, higher levels of alcohol intake, and a longer duration of alcoholism.
In addition to these factors, the severity of beer withdrawal can be exacerbated by:
- Abnormal liver function
- Prior detoxification
- Past experience of seizures or delirium tremens
- Intense craving for alcohol
- Concomitant acute illness
- Advanced age
A better understanding of these factors can aid individuals and healthcare professionals in assessing and managing withdrawal symptoms more effectively.
Fact: Over 50% of individuals experience alcohol withdrawal, especially those with a history of alcohol abuse when they stop or reduce their alcohol consumption, reports Marc A. Schuckit, M.D. of University of California, San Diego, School of Medicine, La Jolla in his review article in New England Journal of Medicine.
Beer Withdrawal Timeline

The timeline for beer withdrawal can vary depending on individual factors, but symptoms generally commence within 6-24 hours after the last drink. Symptoms typically reach their highest intensity within 24-72 hours and cease within 5-7 days.
Bear in mind that the duration of alcohol withdrawal varies among individuals and is influenced by several factors, including the intensity, amount, and frequency of alcohol consumption. Recognizing the timeline of withdrawal symptoms can help individuals and healthcare professionals better prepare for and manage the withdrawal process.
Treatment Options for Beer Withdrawal
Treatment options for managing beer withdrawal symptoms include medical assistance and participation in support groups. The appropriate treatment environment depends on the individual’s needs, abilities, and objectives. Once alcohol withdrawal is diagnosed, appropriate treatment measures can be taken, including assessment, stabilization, and linking to subsequent support.
The following subsections will outline the various treatment options for beer withdrawal, which include medical supervision and detox, outpatient and inpatient treatment programs, support groups and counseling.
Feeling dizzy when trying to give up alcohol? Read our article on dizziness during alcohol withdrawal to find out how to overcome it.
Medical Supervision and Detox
Medical supervision is crucial during the detox process for beer withdrawal, as it aids in:
- Controlling severe symptoms
- Averting potential complications Seeking professional help for alcohol withdrawal is of utmost importance to:
- Manage a person’s physical and mental reactions
- Identify and correct possible metabolic disorders
- Treat other potential complications related to the withdrawal syndrome.
Specialized assistance is required to regulate withdrawal symptoms, and the symptoms can become exacerbated if not managed appropriately. Medical supervision during the detox process can facilitate the management of symptoms, avert potential complications, and guarantee a secure and successful recovery.
Outpatient and Inpatient Treatment Programs
Outpatient treatment for alcohol withdrawal involves receiving care without extended time spent in a hospital or facility, while inpatient treatment is the most intensive form of treatment for alcohol addiction and requires staying in a rehab facility.
Outpatient treatment programs provide greater flexibility and cost-efficiency, while inpatient treatment programs offer more intensive care and assistance. However, outpatient treatment programs may not offer the same level of care and assistance as inpatient treatment programs, and inpatient treatment programs may be costlier and necessitate more time away from home.
Depending on an individual’s specific needs and circumstances, either outpatient or inpatient treatment programs may be more suitable.
Support Groups and Counseling
Support groups and counseling can offer emotional support, provide coping strategies, and facilitate long-term recovery resources for individuals managing beer withdrawal symptoms. Organizations such as Alcoholics Anonymous and Al-Anon provide assistance to those seeking sobriety, offering an opportunity to discuss treatment objectives and difficulties with other individuals in alcohol recovery, and to offer encouragement to sustain sobriety.
Counseling is highly recommended for someone going through alcohol withdrawal, as a counselor can provide guidance on how to manage the psychological and emotional effects of withdrawal and assist someone in preparing for life post-withdrawal. The combination of support groups and counseling can be instrumental in maintaining long-term sobriety.
“Studies demonstrated associated benefits in the following areas: 1) substance use, 2) treatment engagement, 3) human immunodeficiency virus/hepatitis C virus risk behaviors, and 4) secondary substance-related behaviors such as craving and self-efficacy,” reported a meta-analysis of 10 studies. (Benefits of peer support groups in the treatment of addiction, Tracy, Wallace, 2016)
Prevention Strategies for Beer Withdrawal

Preventing beer withdrawal is possible by practicing responsible drinking habits and seeking timely intervention for alcohol use disorders. Abstaining from or limiting exposure to alcohol can help prevent beer withdrawal.
Individuals with alcohol use disorder, which can lead to substance abuse, should reach out to specialized treatment facilities to address their condition. By addressing alcohol dependence early on and making necessary lifestyle changes, individuals can prevent the onset of withdrawal symptoms and ensure a healthier future.
Long-Term Outlook and Recovery After Beer Withdrawal

The long-term outlook and recovery process following beer withdrawal can differ according to the individual. Continued treatment and support, such as attending support group meetings or participating in online support communities, can be instrumental in helping individuals stay abstinent, manage potential relapse triggers, and address any underlying mental health issues.
Potential challenges encountered during the recovery journey may vary for each individual. Addressing alcohol dependence and implementing necessary lifestyle changes are vital to ensure a sustained recovery. By staying committed to ongoing treatment and support, individuals can maintain their sobriety and lead healthier, happier lives.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Beer Withdrawal
Several myths and misconceptions surround beer withdrawal, which can lead to confusion and misinformation. Here are some common myths about beer withdrawal.
- Beer withdrawal is not a serious condition and only affects those who drink heavily.
- Beer withdrawal is less severe than other forms of alcohol withdrawal.
- Beer withdrawal does not cause significant health issues if not managed appropriately.
In reality, beer withdrawal can be as severe as other forms of alcohol withdrawal and may cause significant health issues if not managed appropriately.
Another misconception is the safety of detoxing from alcohol at home, whereas, in reality, specialized assistance is necessary for managing withdrawal symptoms. The symptoms can become exacerbated if not managed appropriately, and it is crucial to seek medical assistance during the detox process to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Summary
In conclusion, understanding beer withdrawal symptoms and treatment options is vital for anyone struggling with alcohol use disorder. By debunking common myths and misconceptions, recognizing the symptoms, seeking appropriate treatment, and maintaining ongoing support, individuals can successfully navigate the challenging journey of beer withdrawal and achieve long-term sobriety. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and the road to recovery is achievable with the right resources and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens when you stop drinking beer for 3 days?
You may experience some withdrawal symptoms such as sweating, shakes, headaches and nausea when you stop drinking beer for 3 days.
You might also have problems with eating and sleeping.
How long does beer take to withdraw?
Beer withdrawal typically occurs within eight hours and peaks between 24 and 72 hours.
It is important to seek medical advice before abruptly stopping drinking.
How do you feel when you stop drinking beer?
Stopping drinking beer can initially lead to mild symptoms such as anxiety, tremors and headaches, followed by more intense cravings and feelings of fatigue and depression.
These symptoms can be difficult to cope with, but there are ways to manage them. Exercise, relaxation techniques, and talking to a therapist can all help reduce the intensity of the cravings and feelings of depression. Additionally, drinking plenty of water.
What is the difference between beer withdrawal and general alcohol withdrawal?
Beer withdrawal is a specific type of alcohol withdrawal that occurs when a person with a chronic alcohol use disorder suddenly stops or significantly reduces their beer intake.
General alcohol withdrawal refers to the effects of quitting any form of alcohol, including beer.
What are some common mild symptoms experienced during beer withdrawal?
Common mild symptoms experienced during beer withdrawal include headaches, anxiety, and irritability.
These symptoms can be difficult to manage, but there are ways to cope. For example, drinking plenty of water, getting plenty of rest, and engaging in physical activity can help.









